Linux InfiniBand
IB网络是RDMA的一种硬件实现,Infiniband是一种专为RDMA设计的网络,从硬件级别保证可靠传输。
Infiniband,支持RDMA的新一代网络协议。 由于这是一种新的网络技术,因此需要支持该技术的NIC和交换机。
因此,如果需要了解Linux下InfiniBand的使用方式,需要先了解RDMA的工作工程。
Linux RDMA core
仓库地址 : Linux RDMA core
libibverbs
可以从构词中发现 lib-ib-verbs,该库是为IB网络定义了RDMA行为。通过IBM提供的手册可以看到对该库的介绍。
Libibverbs库使用户空间进程能够使用远程直接内存访问 (RDMA) 动词。
Libibverbs库在InfiniBand体系结构规范和 RDMA 协议动词规范中进行了描述。
librdmacm
以下是IBM手册对librdmacm的介绍。
librdmacm库提供通信管理器 (CM) 功能和一组通用的远程直接内存访问 (RDMA) CM 接口,这些接口在不同的结构上运行,例如 InfiniBand (IB)、RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE) 或互联网广域网RDMA 协议 (iWARP)。
rc_pingpong源码阅读
rc_pingpong是linux rdma core项目中,libibverbs中的一个案例。基本阐述了InfiniBand Verbs API的使用方法。
程序流程
- 在操作系统中申请资源
- 从Verbs API申请资源
- 使用TCP交换IB连接信息
- 在两个IB端口中创建一个连接
- 在连接上传输数据
- 传输成功
相关函数说明
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9//InfiniBand Devices
struct ibv_device;
// ibv_get_device_list会返回一个可用的IB设备列表。
struct ibv_device **ibv_get_device_list(int *num_devices);
// 打开一个HCA
struct ibv_context *ibv_open_device(struct ibv_device *device);
// 初始化上下文
static struct pingpong_context *pp_init_ctx(struct ibv_device *ib_dev, int size, int rx_depth, int port,int use_event);main函数过程
变量的定义和初始化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43struct ibv_device **dev_list;
struct ibv_device *ib_dev;
struct pingpong_context *ctx;
struct pingpong_dest my_dest;
struct pingpong_dest *rem_dest;
struct timeval start, end;
char *ib_devname = NULL;
char *servername = NULL;
unsigned int port = 18515;
int ib_port = 1;
unsigned int size = 4096;
enum ibv_mtu mtu = IBV_MTU_1024;
unsigned int rx_depth = 500;
unsigned int iters = 1000;
int use_event = 0;
int routs;
int rcnt, scnt;
int num_cq_events = 0;
int sl = 0;
int gidx = -1;
char gid[33];
struct ts_params ts;参数解析
对命令行输入的参数进行解析1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225while (1) {
int c;
static struct option long_options[] = {
{ .name = "port", .has_arg = 1, .val = 'p' },
{ .name = "ib-dev", .has_arg = 1, .val = 'd' },
{ .name = "ib-port", .has_arg = 1, .val = 'i' },
{ .name = "size", .has_arg = 1, .val = 's' },
{ .name = "mtu", .has_arg = 1, .val = 'm' },
{ .name = "rx-depth", .has_arg = 1, .val = 'r' },
{ .name = "iters", .has_arg = 1, .val = 'n' },
{ .name = "sl", .has_arg = 1, .val = 'l' },
{ .name = "events", .has_arg = 0, .val = 'e' },
{ .name = "gid-idx", .has_arg = 1, .val = 'g' },
{ .name = "odp", .has_arg = 0, .val = 'o' },
{ .name = "iodp", .has_arg = 0, .val = 'O' },
{ .name = "prefetch", .has_arg = 0, .val = 'P' },
{ .name = "ts", .has_arg = 0, .val = 't' },
{ .name = "chk", .has_arg = 0, .val = 'c' },
{ .name = "dm", .has_arg = 0, .val = 'j' },
{ .name = "new_send", .has_arg = 0, .val = 'N' },
{}
};
c = getopt_long(argc, argv, "p:d:i:s:m:r:n:l:eg:oOPtcjN",
long_options, NULL);
if (c == -1)
break;
switch (c) {
case 'p':
port = strtoul(optarg, NULL, 0);
if (port > 65535) {
usage(argv[0]);
return 1;
}
break;
case 'd':
ib_devname = strdupa(optarg);
break;
case 'i':
ib_port = strtol(optarg, NULL, 0);
if (ib_port < 1) {
usage(argv[0]);
return 1;
}
break;
case 's':
size = strtoul(optarg, NULL, 0);
break;
case 'm':
mtu = pp_mtu_to_enum(strtol(optarg, NULL, 0));
if (mtu == 0) {
usage(argv[0]);
return 1;
}
break;
case 'r':
rx_depth = strtoul(optarg, NULL, 0);
break;
case 'n':
iters = strtoul(optarg, NULL, 0);
break;
case 'l':
sl = strtol(optarg, NULL, 0);
break;
case 'e':
++use_event;
break;
case 'g':
gidx = strtol(optarg, NULL, 0);
break;
case 'o':
use_odp = 1;
break;
case 'P':
prefetch_mr = 1;
break;
case 'O':
use_odp = 1;
implicit_odp = 1;
break;
case 't':
use_ts = 1;
break;
case 'c':
validate_buf = 1;
break;
case 'j':
use_dm = 1;
break;
case 'N':
use_new_send = 1;
break;
default:
usage(argv[0]);
return 1;
}
}初始化上下文
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11page_size = sysconf(_SC_PAGESIZE);
dev_list = ibv_get_device_list(NULL);
if (!dev_list) {
perror("Failed to get IB devices list");
return 1;
}
...
ctx = pp_init_ctx(ib_dev, size, rx_depth, ib_port, use_event);pp_init_ctx工作过程
在进行这一步之前,已经找到了所需要的IB设备。
pp_init_ctx函数原型分配工作缓冲区1
static struct pingpong_context *pp_init_ctx(struct ibv_device *ib_dev, int size, int rx_depth, int port,int use_event);
打开设备,且创建设备上下文。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9ctx->buf = memalign(page_size, size);
if (!ctx->buf) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't allocate work buf.\n");
goto clean_ctx;
}
设备上下文包含了设备驱动及相关操作。分配保护域(PD, Protection Domain)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11ctx->context = ibv_open_device(ib_dev); // 打开设备
if (!ctx->context) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't get context for %s\n",
ibv_get_device_name(ib_dev));
goto clean_buffer;
}
根据InfiniBand规范,保护域允许客户端在InfiniBand发送和接收期间控制哪些远程计算机可以访问其内存区域。分配内存区域(MR,Memory Region),该区域将被硬件访问。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9ctx->pd = ibv_alloc_pd(ctx->context); // 分配
if (!ctx->pd) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't allocate PD\n");
goto clean_comp_channel;
}创建CQ1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23if (implicit_odp) {
ctx->mr = ibv_reg_mr(ctx->pd, NULL, SIZE_MAX, access_flags);
} else {
ctx->mr = use_dm ? ibv_reg_dm_mr(ctx->pd, ctx->dm, 0,
size, access_flags) :
ibv_reg_mr(ctx->pd, ctx->buf, size, access_flags);
}
if (!ctx->mr) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't register MR\n");
goto clean_dm;
}创建QP1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37if (use_ts) {
struct ibv_cq_init_attr_ex attr_ex = {
.cqe = rx_depth + 1,
.cq_context = NULL,
.channel = ctx->channel,
.comp_vector = 0,
.wc_flags = IBV_WC_EX_WITH_COMPLETION_TIMESTAMP
};
ctx->cq_s.cq_ex = ibv_create_cq_ex(ctx->context, &attr_ex);
} else {
ctx->cq_s.cq = ibv_create_cq(ctx->context, rx_depth + 1, NULL,
ctx->channel, 0);
}
if (!pp_cq(ctx)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't create CQ\n");
goto clean_mr;
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17ctx->qp = ibv_create_qp_ex(ctx->context, &init_attr_ex);
} else {
ctx->qp = ibv_create_qp(ctx->pd, &init_attr);
}
if (!ctx->qp) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't create QP\n");
goto clean_cq;
}总结pp_init_ctx
就是对连接所需的配置,资源进行一个初始化。连接
这部分参考了网上的一些资料,主要是对在远程和本地,对以下三个参数进行配置。 - QPN : QP number,用于标记QB
- LID : Local ID,在Link Layer中被使用,类似于本地的局域网IP地址。
- PSN : Packet Sequence Number,包序列号。用于保证可靠连接。
在main开头,定义了两个结构体具体细节还未整理清楚,但是总体上是完成了下图所示内容。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17//
struct pingpong_dest {
int lid;
int qpn;
int psn;
union ibv_gid gid;
};
// local
struct pingpong_dest my_dest;
// remote
struct pingpong_dest *rem_dest;
且根据函数中细节可以认为,这段配置是通过TCP/IP完成的。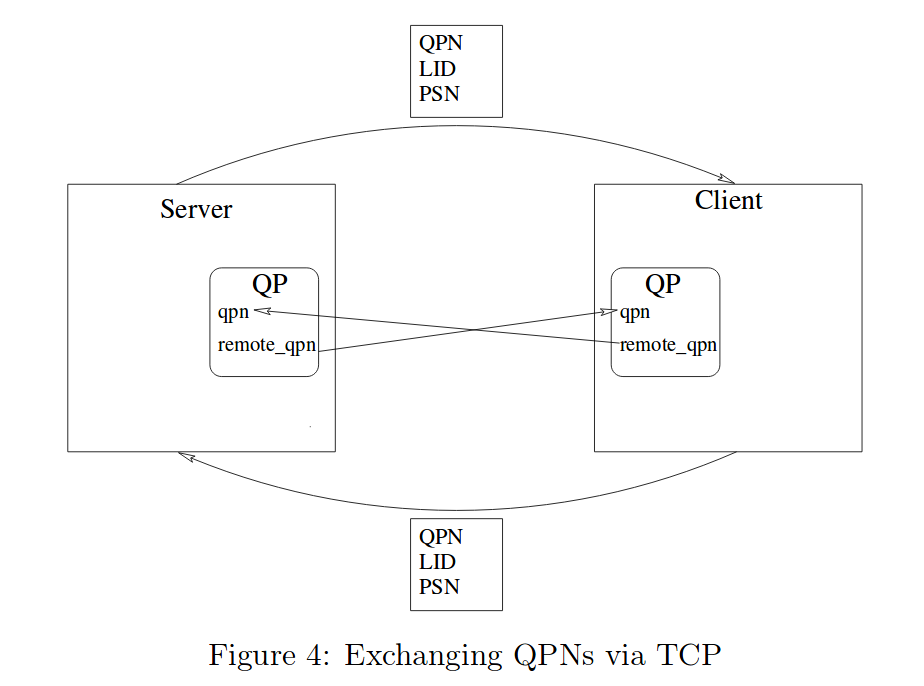
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21//...
// 将my_dest传递给remote
// 似乎是采用了TCP先建立连接。
if (servername)
rem_dest = pp_client_exch_dest(servername, port, &my_dest);
else
rem_dest = pp_server_exch_dest(ctx, ib_port, mtu, port, sl,
&my_dest, gidx);
// ...
// 根据前文的rem_dest配置本地信息
if (servername)
if (pp_connect_ctx(ctx, ib_port, my_dest.psn, mtu, sl, rem_dest,
gidx))
return 1;发送数据
发送数据主要是通过对QP的访问完成的。而pp_post_send最后是通过ibv_post_send函数完成,ibv_post_send在libibverbs/verbs.h中被定义。1
2
3
4
5
6
7if (pp_post_send(ctx)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't post send\n");
return 1;
}而这个ops.post_send可能与RDMA的硬件实现有关。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9static inline int ibv_post_send(struct ibv_qp *qp, struct ibv_send_wr *wr,
struct ibv_send_wr **bad_wr)
{
return qp->context->ops.post_send(qp, wr, bad_wr);
}后续工作
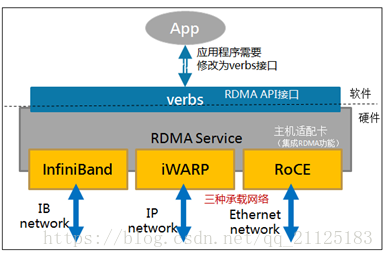
- 本周就是对Linux RDMA core项目做了一定的认识。通过对案例rc_pingpong的分析,对Libibverbs API的使用有了一定的了解。
- 在阅读了深入浅出RDMA博客以后,了解到InfiniBand只是RDMA的一种硬件实现,而实现RDMA还有iWARP和RoCE两种方式。如下所示。