Linux RDMA 内核态Verbs
RDMA Verbs API和Verbs消费者分类
RDMA Verbs不是所有用户都可以任意使用的。RDMA Verbs分为两种,第一种是User-level,另外一种是Privileged。即Verbs API分为用户态和内核态两种。用户态的Verbs API在Linux-RDMA-Core这个项目中被实现。而内核态的Verbs API是集中于Linux内核,形成了Linux Kernel RDMA subsystem。
在InfiniBand的规范定义中,将使用Verbs API的用户分为了两类,第一种是特权级消费者,特权级消费者可以使用所有的Verbs。另外一种是用户级消费者,普通用户只允许使用User-level的Verbs API。
按照InfiniBand规范中的说明,二者的区别如下所示。
- 特权级消费者:需要操作一个特权级别的指令去访问操作系统内部的数据结构,并且实现对Channel接口的控制。
- 用户级消费者:必须要通过其他代理的方式去操作操作系统的数据结构,只能使用特定的Verbs API。
对于Verbs API的级别,在InfiniBand的规范中也有相应的说明。
对于这张表格,第二个标签是实现必要性,如果值为Mandatory,那么就强制要求实现,否则可以选择性实现。
第三个标签Consumer Accessibility则是说明了这条Verbs API需要的权限。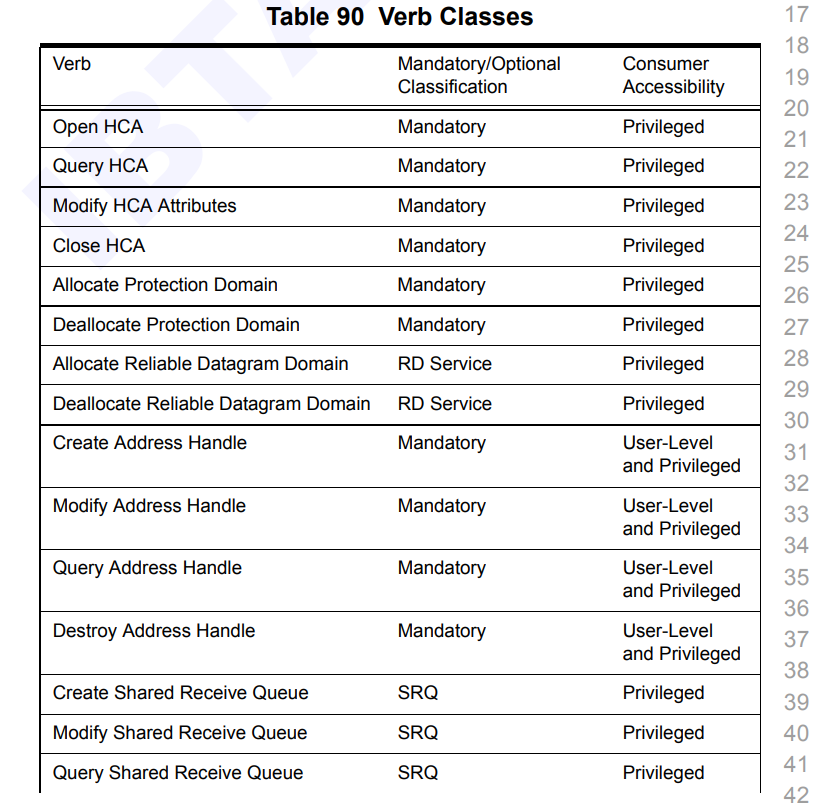
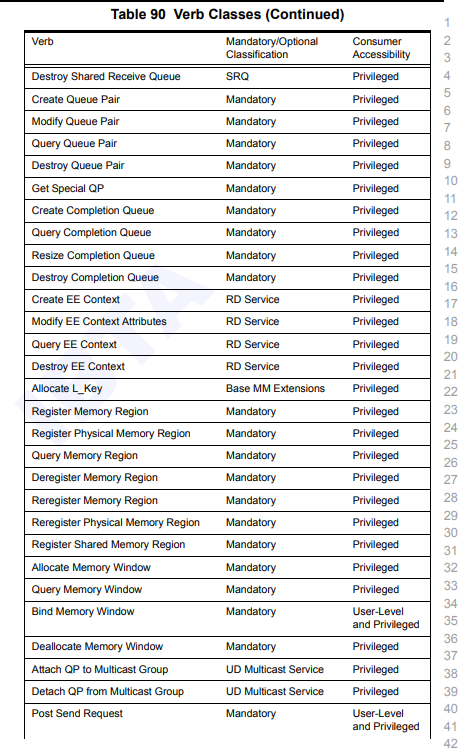
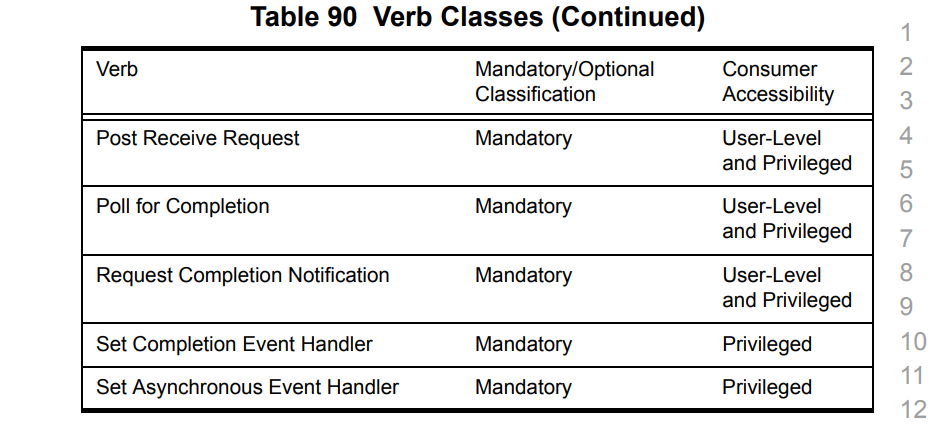
可以从表中看到,User-Level等级的Verbs API不多,一共就以下几个。
用户级别的消费者可以使用的Verbs API为Post Send和Post Recv、对AH的增删查改、绑定Memory Window这几个。 - AH :Address Handle,用于保存地址信息。以指针或者句柄的形式标记一个远程的地址。
我们可以发现,这几个Verbs API的特点都是数据交互相关的,而涉及到对内核数据结构修改,例如QP的增删查改、内存相关的Verbs API,都需要Privileged权限才可以使用。为什么需要内核态Verbs API
参考了一部分的网上资料,总结起来就一句话。为了实现数据的绕开内核功能,需要控制平面在内核做出相应的调整。
控制路径上的调用一般会陷入到内核态,而数据路径上则直接从用户态到硬件。因此Verbs API从功能上来说可以分为数据平面Verbs和控制平面Verbs。总体上,数据平面的Verbs API是所有消费者都可以使用的,而控制平面的Verbs API则只有特权级消费者才能调用。 - 控制平面
- QP的增删查改
- Memory Region的增删查改
- 数据平面
- Post Send
- Post Recv
- Poll CQ
- Bind Memory Window
这部分推测是出于安全的考虑,例如DMA设备注册内存区域这个操作,就需要陷入到内核,不允许普通用户直接使用相关的API注册。不需要经过内核的Verbs API
这部分,我们以Post Send为例,从rdma-core的代码不断向下挖掘分析。
分析rdma-core/libibverbs/examples/rc_pingpong.c文件。这是一个使用rdma-core提供的用户态API实现rdma通信的案例程序。
首先在main函数里,调用了pp_post_send函数,而参数ctx是struct pingpong_context类型的结构体,它的定义如下所示。struct pingpong_context的定义如下所示。它更加仔细的封装了ib在通信时所需要的一些东西。1
2
3
4
5
6
7if (pp_post_send(ctx)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't post send\n");
return 1;
}从pp_post_send继续分析。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39struct pingpong_context {
struct ibv_context *context;
struct ibv_comp_channel *channel;
struct ibv_pd *pd;
struct ibv_mr *mr;
struct ibv_dm *dm;
union {
struct ibv_cq *cq;
struct ibv_cq_ex *cq_ex;
} cq_s;
struct ibv_qp *qp;
struct ibv_qp_ex *qpx;
char *buf;
int size;
int send_flags;
int rx_depth;
int pending;
struct ibv_port_attr portinfo;
uint64_t completion_timestamp_mask;
};在这个位置出现了分支结构,其中涉及到两个send函数,一个是ibv_wr_send,另外一个是ibv_post_send。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59static int pp_post_send(struct pingpong_context *ctx)
{
struct ibv_sge list = {
.addr = use_dm ? 0 : (uintptr_t) ctx->buf,
.length = ctx->size,
.lkey = ctx->mr->lkey
};
struct ibv_send_wr wr = {
.wr_id = PINGPONG_SEND_WRID,
.sg_list = &list,
.num_sge = 1,
.opcode = IBV_WR_SEND,
.send_flags = ctx->send_flags,
};
struct ibv_send_wr *bad_wr;
if (use_new_send) {
ibv_wr_start(ctx->qpx);
ctx->qpx->wr_id = PINGPONG_SEND_WRID;
ctx->qpx->wr_flags = ctx->send_flags;
ibv_wr_send(ctx->qpx);
ibv_wr_set_sge(ctx->qpx, list.lkey, list.addr, list.length);
return ibv_wr_complete(ctx->qpx);
} else {
return ibv_post_send(ctx->qp, &wr, &bad_wr);
}
}
区别该分支的变量为use_new_send,可以从变量名推断,这是用于判断是否是第一次发送数据。ibv_wr_send
调用该函数的情况为use_new_send == 1的情况,根据变量的真实含义推断,该情况应为第一次发送数据的情况。而这里调用了qp结构体的wr_send函数。找到wr_send函数继续向下分析。1
2
3
4
5
6
7static inline void ibv_wr_send(struct ibv_qp_ex *qp)
{
qp->wr_send(qp);
}那么到这里,就无法继续深入了。可以看到,代码声明了一个wqe,而wqe是作为wq的一个元素。那么接下去,就应该是硬件负责的部分了。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33static void wr_send(struct ibv_qp_ex *ibqp)
{
struct rxe_qp *qp = container_of(ibqp, struct rxe_qp, vqp.qp_ex);
struct rxe_send_wqe *wqe = addr_from_index(qp->sq.queue, qp->cur_index);
if (check_qp_queue_full(qp))
return;
memset(wqe, 0, sizeof(*wqe));
wqe->wr.wr_id = qp->vqp.qp_ex.wr_id;
wqe->wr.opcode = IBV_WR_SEND;
wqe->wr.send_flags = qp->vqp.qp_ex.wr_flags;
wqe->ssn = qp->ssn++;
advance_qp_cur_index(qp);
}
并且在rdma-core/providers目录下,出现了mlx5的内容。可以推测,该目录是负责与硬件驱动相关的部分。
翻阅rdma-core/providers/mlx5/qp.c文件,出现了下列相关的代码。我认为也许是与发送wqe相关的操作。这就是说,在rdma-core这个用户态的RMDA Verbs API项目中,也存在与硬件驱动的部分。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39int mlx5_post_send(struct ibv_qp *ibqp, struct ibv_send_wr *wr,
struct ibv_send_wr **bad_wr)
{
if (wr->opcode == IBV_WR_BIND_MW) {
if (wr->bind_mw.mw->type == IBV_MW_TYPE_1)
return EINVAL;
if (!wr->bind_mw.bind_info.mr ||
!wr->bind_mw.bind_info.addr ||
!wr->bind_mw.bind_info.length)
return EINVAL;
if (wr->bind_mw.bind_info.mr->pd != wr->bind_mw.mw->pd)
return EINVAL;
}
return _mlx5_post_send(ibqp, wr, bad_wr);
}
这部分可以说明,在用户态下调用post_send函数,可以直接与相关的硬件进行交互。ibv_post_send
而另外一条路,ibv_post_send函数则与内核态下的内容高度相似,通过调用设备绑定的post_send函数实现该功能。软硬件交汇处,并不是本周的探索重点。但是相信继续往下探索,会出现ibv_context_ops结构体与mlx5设备驱动绑定的地方。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93static inline int ibv_post_send(struct ibv_qp *qp, struct ibv_send_wr *wr,
struct ibv_send_wr **bad_wr)
{
return qp->context->ops.post_send(qp, wr, bad_wr);
}
struct ibv_context_ops {
int (*_compat_query_device)(struct ibv_context *context,
struct ibv_device_attr *device_attr);
int (*_compat_query_port)(struct ibv_context *context,
uint8_t port_num,
struct _compat_ibv_port_attr *port_attr);
void *(*_compat_alloc_pd)(void);
void *(*_compat_dealloc_pd)(void);
void *(*_compat_reg_mr)(void);
void *(*_compat_rereg_mr)(void);
void *(*_compat_dereg_mr)(void);
struct ibv_mw * (*alloc_mw)(struct ibv_pd *pd, enum ibv_mw_type type);
int (*bind_mw)(struct ibv_qp *qp, struct ibv_mw *mw,
struct ibv_mw_bind *mw_bind);
int (*dealloc_mw)(struct ibv_mw *mw);
void *(*_compat_create_cq)(void);
int (*poll_cq)(struct ibv_cq *cq, int num_entries, struct ibv_wc *wc);
int (*req_notify_cq)(struct ibv_cq *cq, int solicited_only);
void *(*_compat_cq_event)(void);
void *(*_compat_resize_cq)(void);
void *(*_compat_destroy_cq)(void);
void *(*_compat_create_srq)(void);
void *(*_compat_modify_srq)(void);
void *(*_compat_query_srq)(void);
void *(*_compat_destroy_srq)(void);
int (*post_srq_recv)(struct ibv_srq *srq,
struct ibv_recv_wr *recv_wr,
struct ibv_recv_wr **bad_recv_wr);
void *(*_compat_create_qp)(void);
void *(*_compat_query_qp)(void);
void *(*_compat_modify_qp)(void);
void *(*_compat_destroy_qp)(void);
int (*post_send)(struct ibv_qp *qp, struct ibv_send_wr *wr,
struct ibv_send_wr **bad_wr);
int (*post_recv)(struct ibv_qp *qp, struct ibv_recv_wr *wr,
struct ibv_recv_wr **bad_wr);
void *(*_compat_create_ah)(void);
void *(*_compat_destroy_ah)(void);
void *(*_compat_attach_mcast)(void);
void *(*_compat_detach_mcast)(void);
void *(*_compat_async_event)(void);
};
以上两条路径,均未发现有以ib_开头的函数,即没有出现调用内核态Verbs API的地方。因此,可以认为,post_send函数是没有经过内核态的。
这里一路看下来,发现post_send完直接到硬件去了,根本没发现数据包封装的细节,这里推测数据包这部分可能是在网卡上完成的。需要经过内核的Verbs API
该章节,以ibv_reg_mr为例,从ibv_reg_mr的定义开始。这里其实非常复杂,参考了一部分网上的资料。
如果直接参考ibv_reg_mr宏的入口,是找不到相关的调用路径的。最终我查阅了资料,发现ibv_cmd_reg_mr函数才是真正进入到内核态的入口。
但是目前还不了解ibv_cmd_reg_mr与ibv_reg_mr之间的关系。
ibv_cmd_reg_mr的定义如下。这里通过write命令写一条命令到操作系统内核。命令的类型就是IB_USER_VERBS_CMD_REG_MR。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79int ibv_cmd_reg_mr(struct ibv_pd *pd, void *addr, size_t length,
uint64_t hca_va, int access,
struct verbs_mr *vmr, struct ibv_reg_mr *cmd,
size_t cmd_size,
struct ib_uverbs_reg_mr_resp *resp, size_t resp_size)
{
int ret;
cmd->start = (uintptr_t) addr;
cmd->length = length;
/* On demand access and entire address space means implicit.
* In that case set the value in the command to what kernel expects.
*/
if (access & IBV_ACCESS_ON_DEMAND) {
if (length == SIZE_MAX && addr) {
errno = EINVAL;
return EINVAL;
}
if (length == SIZE_MAX)
cmd->length = UINT64_MAX;
}
cmd->hca_va = hca_va;
cmd->pd_handle = pd->handle;
cmd->access_flags = access;
ret = execute_cmd_write(pd->context, IB_USER_VERBS_CMD_REG_MR, cmd,
cmd_size, resp, resp_size);
if (ret)
return ret;
vmr->ibv_mr.handle = resp->mr_handle;
vmr->ibv_mr.lkey = resp->lkey;
vmr->ibv_mr.rkey = resp->rkey;
vmr->ibv_mr.context = pd->context;
vmr->mr_type = IBV_MR_TYPE_MR;
vmr->access = access;
return 0;
}然后我们查看Linux内核中的InfiniBand的相关代码。1
2
3ret = execute_cmd_write(pd->context, IB_USER_VERBS_CMD_REG_MR, cmd,
cmd_size, resp, resp_size);
可以在drivers/infiniband/core/uverbs_cmd.c这个目录下找到相关的代码。这里可以找到一个叫做ib_uverbs_reg_mr的函数。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11DECLARE_UVERBS_WRITE(
IB_USER_VERBS_CMD_REG_MR,
ib_uverbs_reg_mr,
UAPI_DEF_WRITE_UDATA_IO(struct ib_uverbs_reg_mr,
struct ib_uverbs_reg_mr_resp),
UAPI_DEF_METHOD_NEEDS_FN(reg_user_mr)),到这里,就可以看到从用户态到内核态的全貌。而用户态和内核态的交互是通过一个叫做ABI的东西实现的。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121static int ib_uverbs_rereg_mr(struct uverbs_attr_bundle *attrs)
{
// 省略前文
// 注册过程
new_mr = ib_dev->ops.rereg_user_mr(mr, cmd.flags, cmd.start, cmd.length,
cmd.hca_va, cmd.access_flags, new_pd,
&attrs->driver_udata);
if (IS_ERR(new_mr)) {
ret = PTR_ERR(new_mr);
goto put_new_uobj;
}
if (new_mr) {
new_mr->device = new_pd->device;
new_mr->pd = new_pd;
new_mr->type = IB_MR_TYPE_USER;
new_mr->uobject = uobj;
atomic_inc(&new_pd->usecnt);
new_uobj->object = new_mr;
rdma_restrack_new(&new_mr->res, RDMA_RESTRACK_MR);
rdma_restrack_set_name(&new_mr->res, NULL);
rdma_restrack_add(&new_mr->res);
/*
* The new uobj for the new HW object is put into the same spot
* in the IDR and the old uobj & HW object is deleted.
*/
rdma_assign_uobject(uobj, new_uobj, attrs);
rdma_alloc_commit_uobject(new_uobj, attrs);
uobj_put_destroy(uobj);
new_uobj = NULL;
uobj = NULL;
mr = new_mr;
} else {
if (cmd.flags & IB_MR_REREG_PD) {
atomic_dec(&orig_pd->usecnt);
mr->pd = new_pd;
atomic_inc(&new_pd->usecnt);
}
if (cmd.flags & IB_MR_REREG_TRANS)
mr->iova = cmd.hca_va;
}
memset(&resp, 0, sizeof(resp));
resp.lkey = mr->lkey;
resp.rkey = mr->rkey;
ret = uverbs_response(attrs, &resp, sizeof(resp));
put_new_uobj:
if (new_uobj)
uobj_alloc_abort(new_uobj, attrs);
put_uobj_pd:
if (cmd.flags & IB_MR_REREG_PD)
uobj_put_obj_read(new_pd);
put_uobjs:
if (uobj)
uobj_put_write(uobj);
return ret;
}ABI
这部分参考了RDMA之用户态和内核态的交互的相关内容。
ABI就是应用程序二进制接口(Application Binary Interface,ABI)。
ABI定义了运行时的程序之间交流的格式,比如参数以什么形式传递(分别写到指定的寄存器/使用栈)、以什么格式传递以及返回值放到哪里等等。
uverbs API规定了用户态和内核态之间的命令消息cmd的格式和返回消息resp的格式。
RDMA软件栈通过设计uverbs ABI接口来保证不同版本的用户态和内核态之间的兼容性,即某个版本的用户态库,可以直接运行在各种版本的内核上。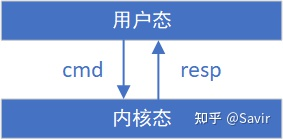
拿Create QP这个函数距离。IB规范上这样定义用户态传入内核态的cmd格式。
resp的定义如下。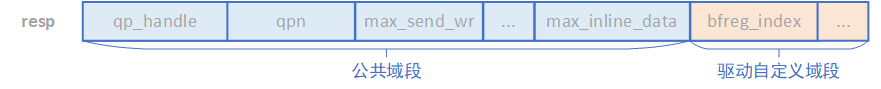
在rdma-core/libibverbs/kern-abi.h文件中有如下定义。看这部分代码,可以看到规定了内核态API和用户态API的映射。例如下列代码。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17DECLARE_CMD(IB_USER_VERBS_CMD_ALLOC_MW, ibv_alloc_mw, ib_uverbs_alloc_mw);
DECLARE_CMD(IB_USER_VERBS_CMD_ALLOC_PD, ibv_alloc_pd, ib_uverbs_alloc_pd);
DECLARE_CMDX(IB_USER_VERBS_CMD_ATTACH_MCAST, ibv_attach_mcast, ib_uverbs_attach_mcast, empty);
DECLARE_CMDX(IB_USER_VERBS_CMD_CLOSE_XRCD, ibv_close_xrcd, ib_uverbs_close_xrcd, empty);
DECLARE_CMD(IB_USER_VERBS_CMD_CREATE_AH, ibv_create_ah, ib_uverbs_create_ah);
DECLARE_CMD(IB_USER_VERBS_CMD_CREATE_COMP_CHANNEL, ibv_create_comp_channel, ib_uverbs_create_comp_channel);
DECLARE_CMD(IB_USER_VERBS_CMD_CREATE_CQ, ibv_create_cq, ib_uverbs_create_cq);
DECLARE_CMD(IB_USER_VERBS_CMD_CREATE_QP, ibv_create_qp, ib_uverbs_create_qp);
// 省略。。。IB_USER_VERBS_CMD_ALLOC_MW是cmd的类型,ibv_开头的函数是用户态的API,而ib_开头的函数是内核态的API。1
DECLARE_CMD(IB_USER_VERBS_CMD_ALLOC_MW, ibv_alloc_mw, ib_uverbs_alloc_mw);
那么可以推测,在该头文件中出现定义的函数,只要调用,那么就需要陷入到内核态里去。总结
本周总结
- 对用户态和内核态的Verbs API做了一定的了解。
- 了解了用户态API与内核态API交互的大体框架。
未实现的
- 了解IB网络数据包封装的细节。
可选的深入的方向
- RDMA通信细节
- 了解RDMA Verbs ABI的内容
- 了解RDMA与IB网卡交互的内容
下周工作
按照张老师意见,IB数据包应该是在驱动里面完成封装的,可以具体看看驱动的代码。
